A powerful, easily deployable network traffic analysis tool suite for network security monitoring
Automatic file extraction and scanning
Malcolm can leverage Zeek’s knowledge of network protocols to automatically detect file transfers and extract those files from PCAPs as Zeek processes them. This behavior can be enabled globally by modifying the ZEEK_EXTRACTOR_MODE variable in zeek.env, or on a per-upload basis for PCAP files uploaded via the browser-based upload form when Analyze with Zeek is selected.
To specify which files should be extracted, the following values are acceptable in ZEEK_EXTRACTOR_MODE:
none: no file extractioninteresting: extraction of files with mime types of common attack vectors (recommended)notcommtxt: extraction of all files except common plain text filesall: extract all filesmapped: extraction of files with recognized mime typesknown: extraction of files for which any mime type can be determined
Depending on the volume of files extracted from network traffic, file scanning can be resource-intensive. When enabled, it is recommended to select interesting or notcommtxt unless running on a high-performance system.
Extracted files are scanned by Strelka, an open-source “real-time, container-based file scanning system used for threat hunting, threat detection, and incident response.”
Individual Strelka scanners can be toggled or configured by editing strelka/config/backend/backend.yaml. To disable a scanner, comment it out by adding # to each line of its section under scanners:, including the scanner’s name:
⋯
scanners:
⋯
# 'ScanDocx':
# - positive:
# flavors:
# - 'application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document'
# - "docx_file"
# priority: 5
# options:
# extract_text: False
⋯
To enable a scanner, uncomment its section:
⋯
scanners:
⋯
'ScanDocx':
- positive:
flavors:
- 'application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document'
- "docx_file"
priority: 5
options:
extract_text: False
⋯
It’s recommended to validate this configuration file after making changes to it. This could be done using an online YAML validator or locally depending on available tools:
python3 -c 'import sys, yaml; yaml.safe_load(sys.stdin)' < ./strelka/config/backend/backend.yamlruby -ryaml -e "YAML.load_file('./strelka/config/backend/backend.yaml')"
Each scanner may have configurable options; see the scanner list for more details. Other Strelka-related configuration files can be found under strelka/config/. Consult the Strelka documentation for more details.
For the YARA scanner, Malcolm’s default YARA rule set and/or user-defined custom YARA rules are used for scanning.
The RULES_UPDATE_ENABLED environment variable in pipeline.env controls whether or not to regularly pull signature/rule definitions from the internet for file scanning engines, including ClamAV signatures and Malcolm’s default YARA rule set.
The FILESCAN_PRESERVATION environment variable in filescan.env determines the behavior for preservation of scanned files:
quarantined: preserve only files in./zeek-logs/extract_filesthat are flagged by the YARA, ClamAV, or Capa scannersall: preserve all extracted files files in./zeek-logs/extract_filesnone: preserve no extracted files
The FILESCAN_HTTP_SERVER_… environment variables in filescan.env and filescan-secret.env configure browsing and download access to the scanned files through the means of a simple HTTPS directory server accessible at https://localhost/extracted-files/ if connecting locally. Beware that these files may contain malware. As such, these files may be optionally ZIP archived (without a password or password-protected according to the WinZip AES encryption specification) or encrypted (to be decrypted using openssl, e.g., openssl enc -aes-256-cbc -d -in example.exe.encrypted -out example.exe) upon download. In other words:
- to disable the extracted files server:
FILESCAN_HTTP_SERVER_ENABLE=false
- to enable the extracted file server:
FILESCAN_HTTP_SERVER_ZIP=true- downloaded files are zipped, without a password:
FILESCAN_HTTP_SERVER_ZIP=trueFILESCAN_HTTP_SERVER_KEY=
- downloaded files are zipped, AES-encrypted with a password:
FILESCAN_HTTP_SERVER_ZIP=trueFILESCAN_HTTP_SERVER_KEY=xxxxxxxxxxxxx
- downloaded files are OpenSSL AES-256-CBC-compatibly encrypted:
FILESCAN_HTTP_SERVER_ZIP=falseFILESCAN_HTTP_SERVER_KEY=xxxxxxxxxxxxx
- downloaded files are downloaded as-is, without archival or compression:
FILESCAN_HTTP_SERVER_ZIP=falseFILESCAN_HTTP_SERVER_KEY=
User interface
The files extracted by Zeek and the data about those files can be accessed through several of Malcolm’s user interfaces.
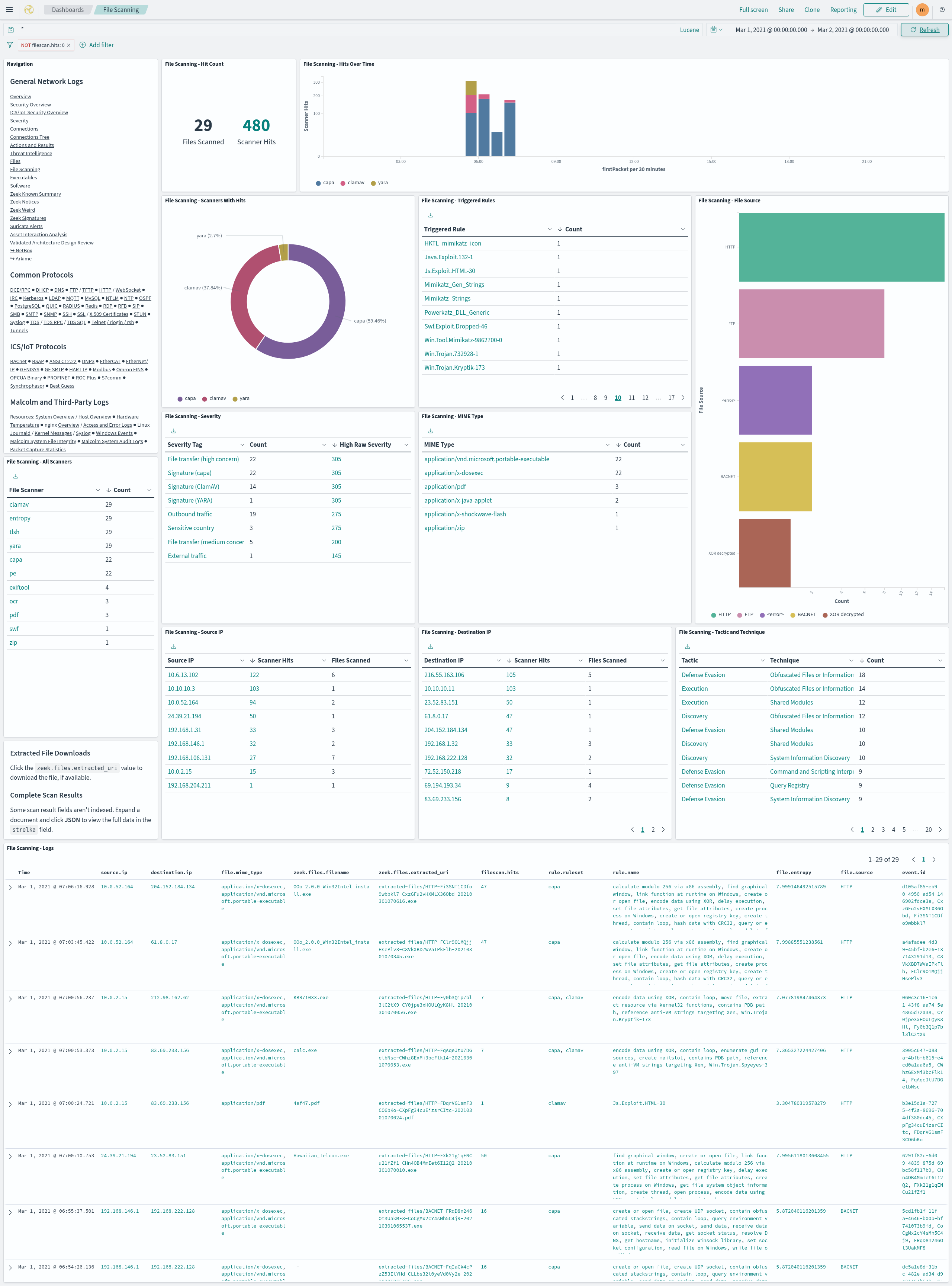
- The File Scanning dashboard summarizes the results of the file scans performed by Strelka.
- Click a
zeek.files.extracted_urivalue in the File Scanning - Logs table to download the associated file, if available. Note that the presence of these links don’t necessarily imply that the files they represent are available: depending on factors such as file preservation settings (above) and retention policies, files that were extracted and scanned may no longer be available. When this is the case, clicking one of the file download links will result in a “file not found” error. If one of these links refers to a file that was extracted and scanned on a Hedgehog Linux network sensor, Malcolm must be able to communicate with that sensor in order to retrieve and download the file. - Some scan result fields aren’t indexed. Expand a document and click JSON to view the full scan result’s data in the
strelkafield.
- Click a
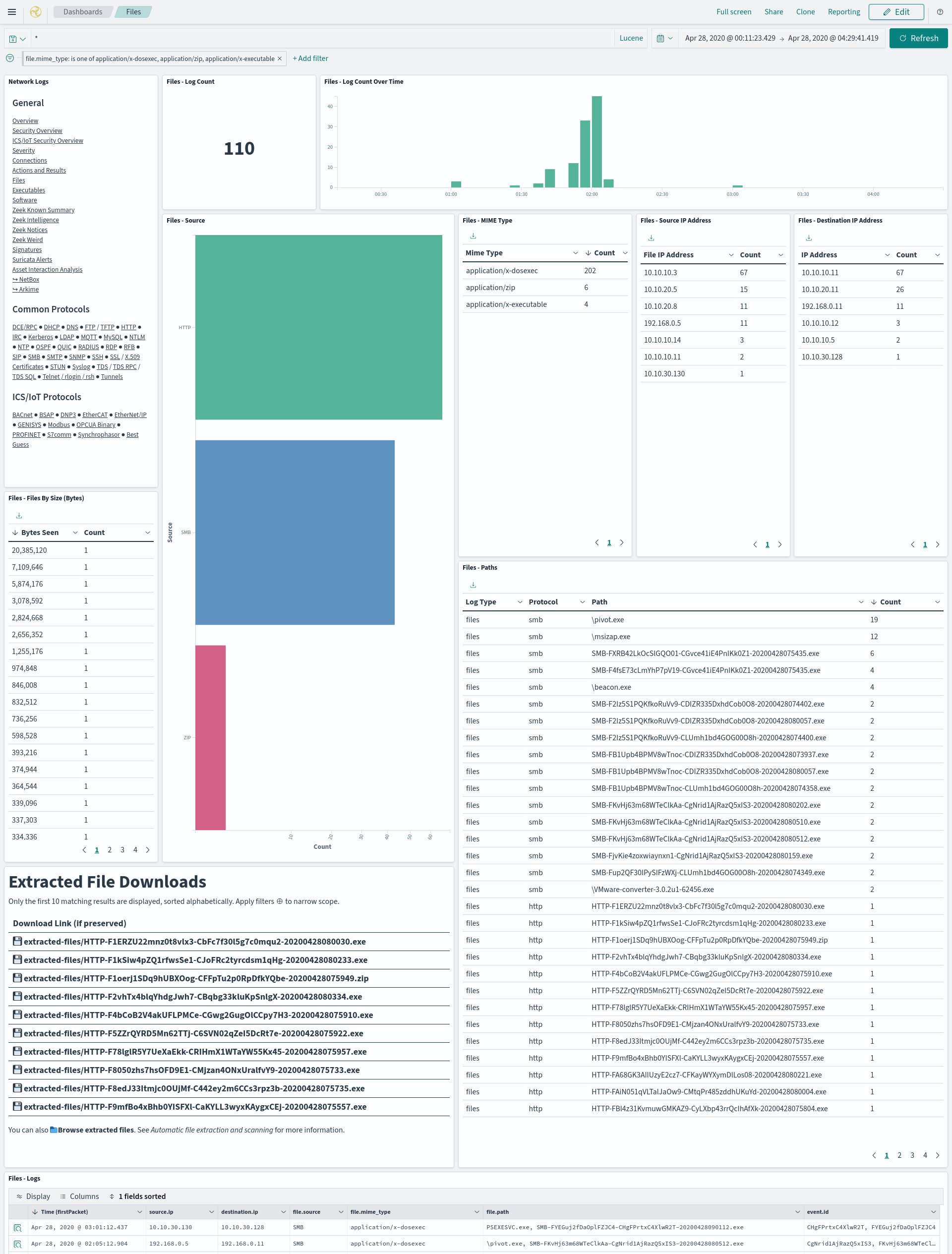
- The Files dashboard summarizes the file transfers observed in network traffic.
- The Extracted File Downloads table provides download links for the extracted files matching the currently applied filters, if it was preserved as described above.
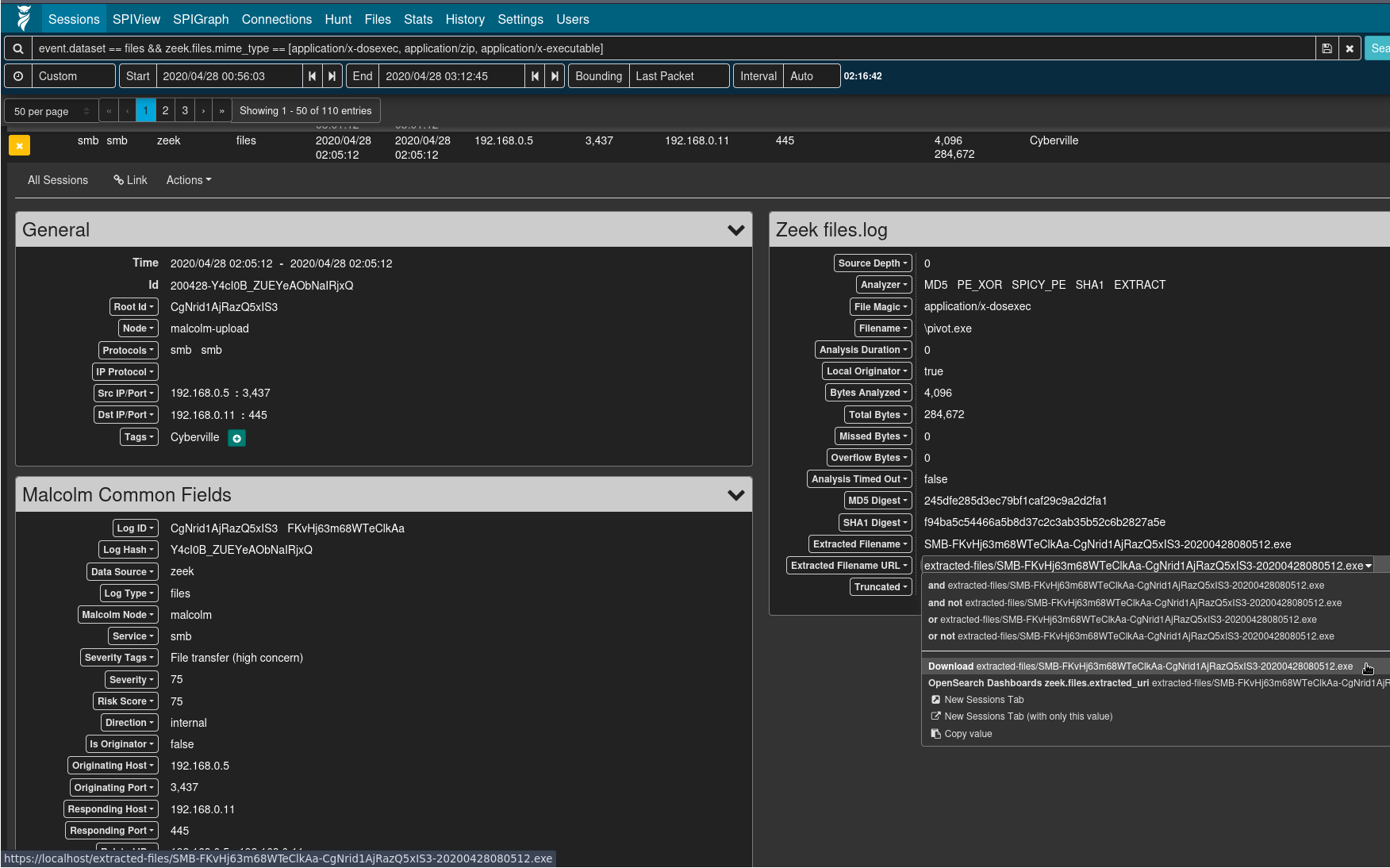
- Viewing logs from Zeek’s
files.log(e.g.,event.provider == zeek && event.dataset == files) or the file scan results (e.g.,event.provider == filescan), the Arkime session detail’s Extracted Filename URL field can be clicked for a context menu item to download the extracted file, if it was preserved as described above.
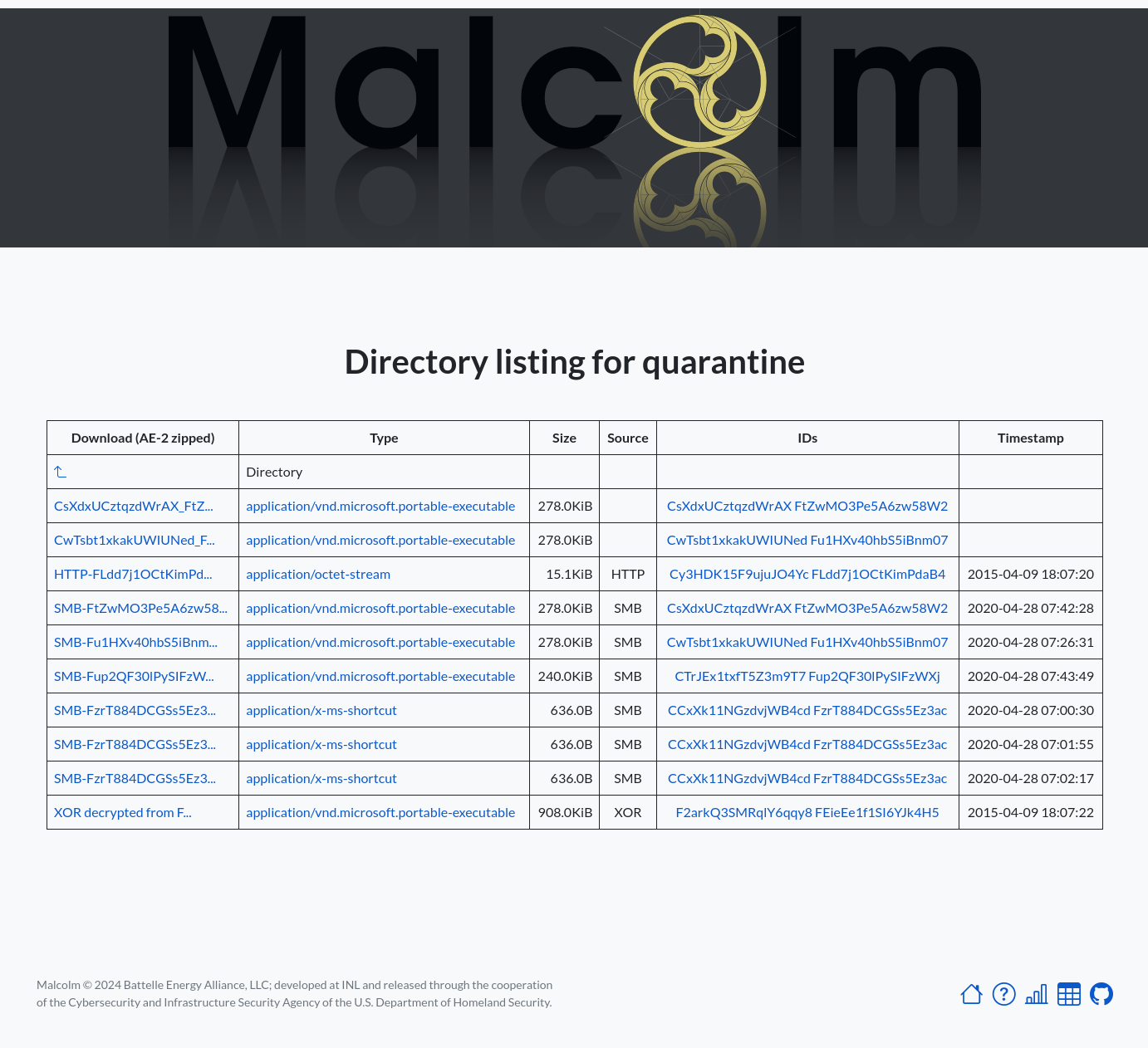
- Malcolm provides an extracted files directory listing to browse and download Zeek-extracted files. This interface is available at https://localhost/extracted-files/ if connecting locally. The Zeek
uidandfuidvalues associated with these files and the sessions from which they were extracted are listed in the IDs column as filter links back into Dashboards. Similarly, files extracted and preserved on a Hedgehog Linux network sensor can be accessed at https://localhost/hh-extracted-files/X.X.X.X/, where X.X.X.X represents the IP address or hostname of the sensor (e.g.,https://localhost/hh-extracted-files/192.168.122.57/if the sensor’s IP address were 192.168.122.57).